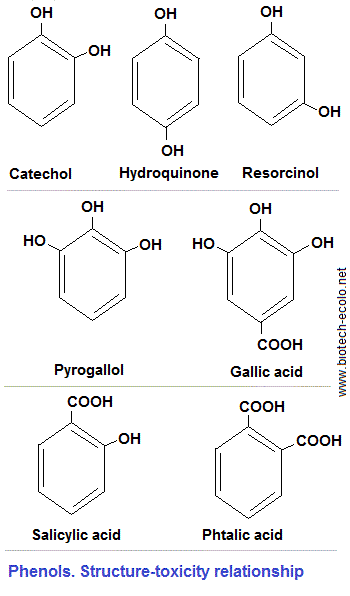
Plant resistance reactions against fungi. Biochemical and molecular aspects of relations between hosts and pathogens
Aspects biochimiques et moléculaires de la résistance des plantes aux attaques des champignons
....plant resistance, fungi, pathogens